In this article we will talk about : Acute bronchitis causes, symptoms and treatment.
Contents
Acute bronchitis definition
The acute bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchi. It is characterized by a cough, with or without fever and / or sputum (secretions commonly called “sputum”).
Bronchitis is one of the most common respiratory conditions (it occurs at least once in a lifetime).
For the most part, it has no health consequences. However, This disease can worsen due to an immune deficiency, bacteria, age and smoking.
Fragile people (those over 65, or suffering from chronic pulmonary disease such as COPD, asthma, respiratory failure, etc.) are particularly vulnerable.
Acute bronchitis causes
The acute bronchitis are viral in 90% of cases, while bacteria in the remaining 10%.
They appear, most often, following a cold, flu or nasopharyngitis.
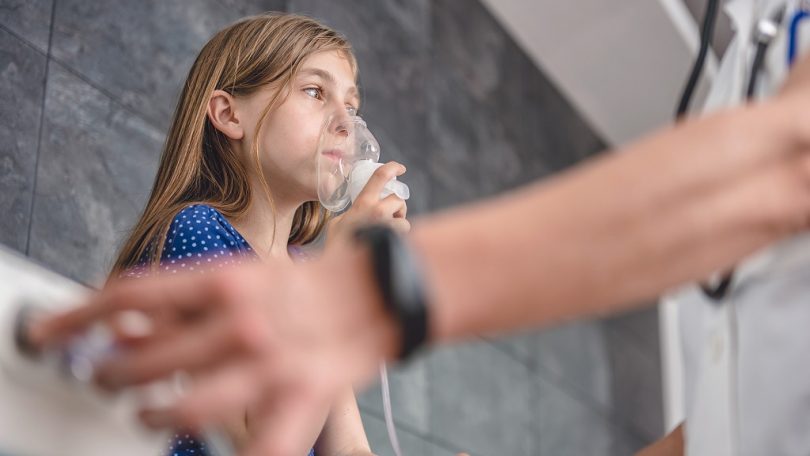
Acute bronchitis symptoms
The main symptom of this disease is cough.
At first, the cough is dry, then it quickly becomes greasy and persistent with expectoration of thick yellowish or greenish mucus.
Can also occur:
- fever;
- respiratory discomfort;
- muscle pain;
- tiredness;
- a burning sensation in the chest.
In a fragile person (immunocompromised for example) or suffering from asthma, chronic bronchitis (COPD) or other pulmonary disease, the appearance of acute bronchitis quickly requires medical consultation, to prevent any complications.
Acute bronchitis prevention councils
To prevent the occurrence of acute bronchitis , it is important to follow these tips:
- avoid cold and humid environments;
- stop smoking;
- limit exposure to air pollution and tobacco smoke as much as possible;
- try to strengthen the immune system (rest, adapted and balanced diet, regular physical exercise).
Acute bronchitis exams
The acute bronchitis usually disappears within a few days.
However, it is necessary to consult a doctor in the event of:
- persistent fever;
- chest pain with shortness of breath;
- coughing up blood or if there is any doubt about pneumonia (pulmonary infection).
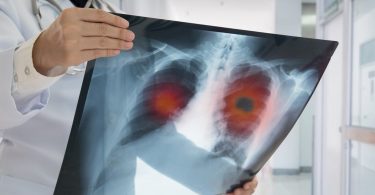
A chest x-ray will be performed and, if necessary, additional examinations will be performed (sputum analysis, scanner, etc.)
Acute bronchitis treatment
The treatment of acute bronchitis in a healthy subject usually includes:
- good hydration;
- fever medication (paracetamol);
- cough suppressants only in the evening, to promote sleep;
- fluidizers during the day;
- drops to unclog the nose;
- syrup or sucking tablets for pain in the throat.
Sometimes bronchodilators are used.
Antibiotics, useless at the start of this disease
Antibiotics are generally unnecessary at the start of acute bronchitis because they cannot fight viruses.
They are established if bacterial bronchitis is suspected, if the patient has a known underlying lung disease or is a subject at risk (immunocompromised, etc.), or if there is a pulmonary infection.
Respiratory physiotherapy sessions may be prescribed, especially in young children.
What about a persistent cough?
If the cough persists for more than 2 weeks, it is necessary to consider whooping cough or a non-infectious origin to cough (asthma, etc.).
If no other cause is found, treatment with corticosteroids for a few days can help make it go away.
Homeopathy
When this disease is chronic, a basic homeopathic treatment is essential with regular doses of Thuja and Natrum sulfuricum in 9 CH, one dose per week alternately for several months:
- In acute phase: Ferrum phosphoricum, 9 CH, 5 granules morning and evening while waiting to consult.
- To relieve coughing spells and promote sputum: Antimonium tartaricum, 9 CH, and Ipeca, 9 CH alternately 5 granules three times a day.
- To thin mucus: Kalium bichromicum, 9 CH, 5 granules every two hours for 48 hours, then twice a day until symptoms improve.
Phytotherapy
Choose plants that treat the respiratory and hepatic spheres (depurative plants):
- In mother tincture: eucalyptus, white horehound and plantain, take 25 drops three times a day in a little water.
- In herbal tea: eucalyptus, coltsfoot, poppy (respiratory tract), berberis (liver), fumitory (depurative), 4 tablespoons of this mixture per liter of water. Drink one liter per day until improvement.
Aromatherapy
To relieve symptoms of this disease :
- Mix essential oils of common myrtle with cineole (2 drops), tea-tree (2 drops), satureioid thyme (2 drops) and ravensare (1 drop). For adults: 6 drops of the massage mixture on the chest.
- Inhalation: 6 drops of cajeput essential oil in a bowl of boiling water.
Please note, restrictions exist for children under 6 and pregnant women. Imperatively to see the precautions for use of any essential oil before use.
Read also: Cancer: causes, symptoms and treatment