In this article we will talk about : Asthma causes, symptoms and treatment.
Contents
Asthma definition
The asthma in general, is a chronic inflammatory airway disease. It results in difficulty breathing (dyspnea).
During the asthma attack , the diameter of the bronchi decreases, which interferes with normal air circulation and causes wheezing.
Asthma usually goes away with age
Asthma affects approximately 3-5% of adults and 10% of children. The disease affects twice as many boys as girls before puberty. A family predisposition exists quite frequently.So, asthma is a reversible disease that usually goes away with age.
Asthma is commonly confused with COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) which is, on the contrary, irreversible.
The main complication of the asthma attack is severe acute asthma which is resistant to commonly prescribed medications. For this reason, he demands emergency treatment.
Asthma causes
The cause of asthma is not always identified. However, there are risk factors that can trigger a crisis:
- an allergy (to pollen, dust, animal hair, etc.);
- physical activity or effort;
- certain inflammatory drugs including aspirin;
- an infection ;
- the stress ;
- anger ;
- excitement;
- strong emotions.
Air pollution could also, play a role .
It can be caused by effort ( asthma of effort ).
The mechanisms behind asthma
At the origin of the bronchial obstruction, characteristic of the asthma attack , several mechanisms have been highlighted such as:
- an inflammation of the bronchi with an excessive quantity of mucus produced by the mucous membrane and a thickening of the wall of the bronchi (edema);
- a contraction of the muscles of the wall of the bronchi also called bronchial hyperreactivity.
Asthma symptoms
The people with mild asthma have no symptoms between attacks. On the contrary, those affected by a more severe form may suffer from continuous respiratory discomfort, often aggravated at night.
Symptoms of the asthma attack
The most common symptoms of an asthma attack are:
- difficulty breathing on expiration;
- wheezing ;
- chest tightness;
- wheezing ;
- increase or decrease in respiratory rate;
- dry irritating cough, sometimes chronic;
- increased heart rate;
- shortness of breath,
- pursed lips;
- difficulty expressing oneself;
- excessive sweating;
- significant anxiety.
If the crisis is severe (severe acute asthma ), respiratory failure (disturbances of consciousness, bluish discoloration of the skin, etc.) can appear suddenly and lead to a risk of death by asphyxiation. So, you must urgently call a doctor or the Samu.
Asthma prevention councils
In order to reduce the frequency of seizures, the asthmatic person must adopt a healthy lifestyle:
- work on breathing (breathing exercises);
- practice a physical activity, preferably an endurance sport in order to work the cardiorespiratory system;
- quit smoking and avoid smoky places (a rule which also applies to those around you);
- limit or avoid contact with the allergens responsible (mites, dust, animals, etc.): ventilate daily, avoid carpets and rugs, dust your home, etc.
Follow-up of the background treatment ordered by the doctor is also essential.
Since July 2013, it is recommended that people suffering from severe asthma and under continuous treatment be vaccinated against pneumococcus because of the high risk that they have of contracting an invasive pneumococcal infection. This vaccine in fact protects 80% against pneumococcal pneumonia (23 kinds of pneumococci out of 90).
Asthma exams
The diagnosis of asthma includes:
- a respiratory functional exploration (FRT), in order to assess the severity of the disease;
- a chest x-ray, to rule out other pathologies;
- an allergological assessment (skin tests), looking for a possible allergic cause of asthma.
During crises, the triggering factors must be found as much as possible (infection, stress, etc.).
Asthma treatment
In a person suffering from asthma, a basic treatment is always recommended because it improves the quality of life. Its objective is to decrease the inflammation of the bronchi, which is the cause of chronic disease. It consists of a daily intake of:
- inhaled corticosteroids;
- bronchodilators;
- antihistamines;
- or other specific asthma medications (antileukotrienes).
For the most part, measuring peak expiratory flow (using a peak flow meter) is useful for assessing respiratory capacity and detecting an attack early. Available in pharmacies, the flow meter is an easy-to-use portable device.
Treatment for asthma attack
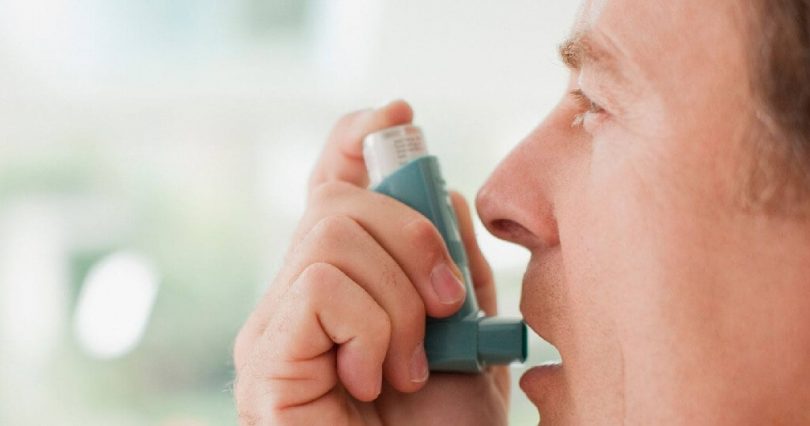
overall, the subject with an asthma attack can use a spray bronchodilator or inhaler that he usually has on him to stop the attack. Even when the crisis stops, it is best to tell your doctor.
If no cause is found or if the attacks are repeated, it is necessary to carry out an assessment in consultation in order to modify the usual treatment.
In conclusion, if the attack seems more severe or cannot be stopped by the spray, hospitalization is necessary. The doctor will then use bronchodilators in the form of aerosols or by injection, anti-inflammatory drugs by infusion, or even oxygen.
Phytotherapy
Certain herbal preparations can usefully complement (and without interference) the basic treatments essential to treat a chronic pathological condition such as asthma. For example:
- In infusion: white flower broth. Put 30 g in 1 liter of water, let infuse for 10 minutes. 1 to 2 cups a day.
- In infusion: hyssop flowering tops. Put 30 g in 1 liter of water, leave to infuse for 10 minutes, filter carefully. 1 to 2 cups a day.
- In infusion: mixture of plants associating hyssop flowering tops 20 g, ballote flowering tops 20 g, poppy flowers 20 g. Put 1 tablespoon of the mixture in 125 ml of water, leave to infuse for 10 minutes. 2 to 3 cups per 24 hours.
Read also:
Panic attack: causes, symptoms and treatment
How to protect from colds, flu and gastroenteritis
Asthma: causes, symptoms and treatment
Ascites: causes, symptoms and treatment
Asbestosis: causes, symptoms and treatment
Osteoarthritis: causes, symptoms and treatment