Very common in children under 10, tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils. Discomfort when swallowing and sore throat are its main warning signals. In this article, We will talk about tonsillitis causes, symptoms and treatment.
Contents
Tonsillitis definition
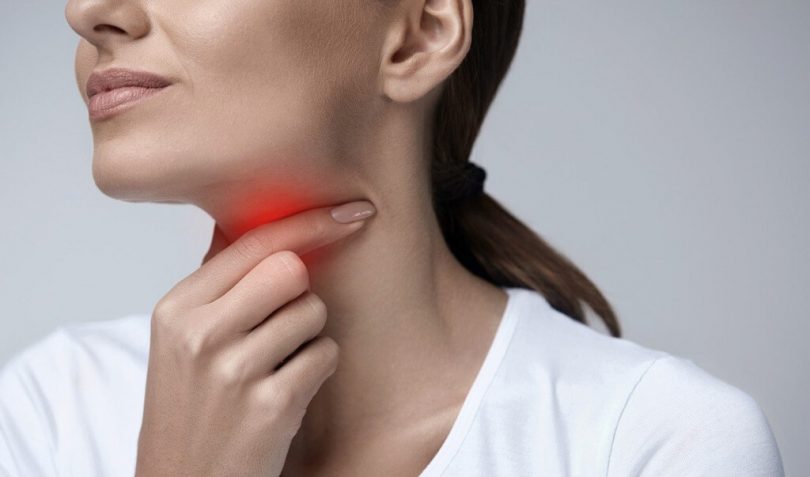
As the name suggests, tonsillitis is an inflammation (acute or chronic) of the tonsils , a set of lymph nodes located at the back of the throat.
Tonsillitis is more common in children under 10 years of age. In adults, it most often occurs in summer, when there are large changes in temperature.
The most serious complication of acute tonsillitis is the tonsil phlegmon , a pocket of pus that collects at the level of the veil, in front of the tonsils. It can cause a constant and involuntary contraction of the jaw muscles (trismus) which no longer allows the mouth to be opened.
Tonsillitis causes
The most common culprits of viral tonsillitis are respiratory cold or flu viruses (adenovirus, rhinovirus, influenza , coronavirus). Tonsillitis can also be caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (which causes infectious mononucleosis ).
The second most common cause is bacterial, with group A beta-hemolytic group streptococcus, responsible for strep throat .
Tonsillitis symptoms
The main symptoms of tonsillitis are:
- sore throat ;
- feeling of discomfort, foreign body in the throat;
- pain when swallowing;
- fever, when there is an infection.
Sometimes there are other symptoms:
- red and / or swollen tonsils;
- irritated voice and throat;
- white or yellow spots on the tonsils;
- difficult and painful swallowing;
- bad breath;
- swollen lymph nodes (in the neck).
Tonsillitis prevention councils
To prevent the onset of tonsillitis, it is possible to act on its direct causes. It is therefore necessary to avoid as much as possible, even if it is sometimes difficult, viral and bacterial infections.
To this end, the following hygiene tips may be useful:
- teach children to wash their hands (with soap and water for 30 seconds) and encourage them to do so before a meal and after using the toilet;
- cover his mouth in case of coughing or sneezing (in the crease of the elbow) and teach this technique to children;
- have good dental hygiene.
Tonsillitis exams
It is important to get a quick and accurate diagnosis because the treatment for tonsillitis depends on its cause.
During the clinical examination, if the patient opens his mouth, the doctor can see red and swollen tonsils at the back of the throat . This inflammation associated with sore throat indicates the presence of tonsillitis.
In the presence of signs of infection (whitish coloration of the tonsils, fever, etc.), we can take a sample from the throat to look for a germ, in particular streptococcus of the beta-hemolytic group of group A. This sample is useless if the tonsillitis only causes discomfort.
Without signs of infection, blood tests are not helpful.
Tonsillitis treatment
As tonsillitis is most often caused by a virus, antibiotics are not helpful.
However, when signs of bacterial infection appear, especially fever and persistent pain, and after having the patient take a test for bacteria, the doctor may prescribe antibiotic therapy.
To relieve the pain, it is possible to take analgesics (paracetamol) and to act locally (rehydration with hot drinks, gargles of salt water …).
The tonsil phlegmons generally require surgical drainage of the abscess.
The large tonsils in adults can also be reduced:
- laser;
- by radio frequency: under local anesthesia, the doctor uses a process that burns the superficial part of the tonsils and reduces their size. This treatment can sometimes be enough, especially in crypto-caseous tonsillitis (with the presence of small holes where food can lodge or small smelly yellowish debris).
A surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) is performed:
- if children do not respond to antibiotics;
- in case of chronic tonsillitis, and when the tonsils are obstructive (large tonsils): the latter can interfere because they block the upper airways when lying down;
- in case of recurrent tonsillary infections.
This operation is considered today as a measure of last resort because it is not trivial.
Most often, acute tonsillitis goes away on its own. Healing takes a few days in case of classic bacterial or viral tonsillitis, but it can take weeks if mononucleosis is involved.
Read also:
Acne : causes, symptoms and treatment