Diabetes is a chronic disease resulting in too high blood sugar. A distinction is made between type 1 diabetes which manifests itself in childhood or adolescence, that of type 2 generally occurring after 40 years, and gestational diabetes during pregnancy. In this article we will talk about : Diabetes symptoms, causes and treatment.
Contents
Diabetes definition
Whatever its type, diabetes is a disorder of the assimilation and use of the sugars contained in food and which provide the energy essential for the organism to function.
Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, normally allows glucose to enter the body’s cells for energy. When the insulin is insufficient, the whole system goes wrong.
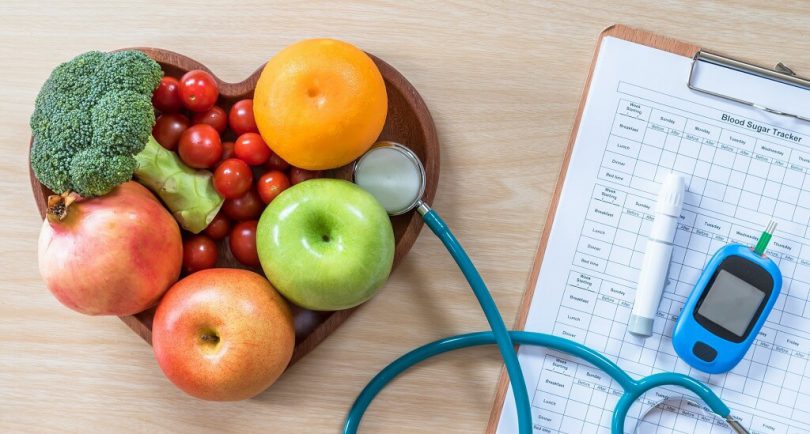
Poorly assimilated, sugars then accumulate in the blood. The glycemia, which measures the presence of glucose (sugar) in the blood, becomes too high: the rate is greater than 1.26 g / l (7.7 mmol / l) during a fasting dosage or greater than 2g / l at any time of the day. We then speak of hyperglycemia.
Ultimately, this hyperglycemia can cause complications that can be serious, particularly in the blood vessels, heart, eyes, kidneys … People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing an infection. It is also possible that too high a hyperglycemia could lead to comas.
Three types of diabetes
Type 1 diabetes, also called insulin-dependent diabetes, affects less than 10% of the population and occurs in childhood or adolescence, sometimes in adulthood.
The most common type 2 diabetes manifests later, from the age of 40.
Finally, diabetes can develop during pregnancy, it is gestational diabetes. In the vast majority of cases, it disappears after childbirth.
Diabetes has experienced unprecedented development for several years, the World Health Organization going so far as to use the term “epidemic”.
Diabetes causes
In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas, due to self-destruction of some of its cells called islets of Langerhans, is unable, in whole or in part, to make insulin. It is an autoimmune disease. The cause of the destruction of the islets of Langerhans is not well known.
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas produces insulin well, but it acts badly, the body becomes resistant to insulin.
There is a genetic predisposition to type 2 diabetes: having a diabetic parent doubles the risk. Taking certain medications, hormonal or pancreatic disease may be involved.
Other risk factors for type 2 diabetes include:
- lack of physical activity;
- obesity or significant weight gain;
- the existence of a history of gestational diabetes;
- a child born with a weight greater than 4 kg.
The roles of diet and lifestyle in triggering this diabetes have been clearly demonstrated.
Diabetes symptoms
Type 2 diabetes is a silent disease, that is, it develops without symptoms for many years. It can be detected during an ordinary biological check-up. Otherwise, it is when the first complications appear that the diagnosis is made.
As for type 1 diabetes, which affects young people, its main manifestations are:
- intense thirst;
- significant urges to urinate,
- rapid and unexplained weight loss.
It requires an emergency diagnosis, especially for children.
Diabetes prevention councils
Unlike type 1 diabetes which is an autoimmune disease, it is possible to reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by acting on the factors that promote it, namely an unbalanced diet and a sedentary lifestyle.
In case of overweight, a major risk factor for this diabetes, it is strongly recommended to lose weight by following an adapted diet and by practicing regular physical activity.
Diabetes exams
The diagnosis of diabetes is based on:
- measurement of glycemia (blood sugar level) on an empty stomach or after absorption of a sugar solution;
- a full medical examination in order to detect any complications.
Diabetes treatment
Regardless of the type of diabetes, the goal of treatment is to normalize blood sugar to prevent the serious complications associated with this disease.
Treating type 1 diabetes involves providing the body with the insulin it needs, since the pancreas is unable to make it. Daily administration of insulin is by subcutaneous injection (doses are adjusted according to physical activity and diet) or via an insulin pump.
The management of type 2 diabetes is firstly based on following an adapted diet and practicing regular physical activity. The therapeutic education of the patient is an important element of this management.
If these measures are not enough to lower the blood sugar level, the doctor will prescribe oral and non-insulin medication. The health recommendations recommend prescribing metformin alone as a first line. Since type 2 diabetes is an active disease, dual therapy and then triple therapy may be considered later on the basis of a combination of metformin and sulphonylurea.
When oral treatments are no longer sufficient, insulin becomes the standard treatment.
Read also:
How to lower cholesterol ?